What is location intelligence technology and how can it help you grow your business
For organisations that want to understand how people interact with physical locations, location intelligence is the answer. It takes business analytics to the next level by revealing patterns and trends hidden in location-based data, enabling organisations to gain actionable insights that drive growth, efficiency and innovation.
In this article, we’ll dive into the location intelligence technology, examining how it works, its essential components, and the transformative impact it can have on an organisation’s growth.
What is location intelligence and how does it work?
Location intelligence (LI) technology is an advanced analytical tool that integrates geographic data with various business-relevant datasets to introduce valuable insights. It goes beyond traditional Geographic Information Systems (GIS) by combining spatial information with data from multiple sources, such as geographic information, traffic patterns, customer data, social media, and economic statistics. This data is then processed using advanced algorithms and visualisation tools to reveal trends, and correlations that are not immediately apparent.
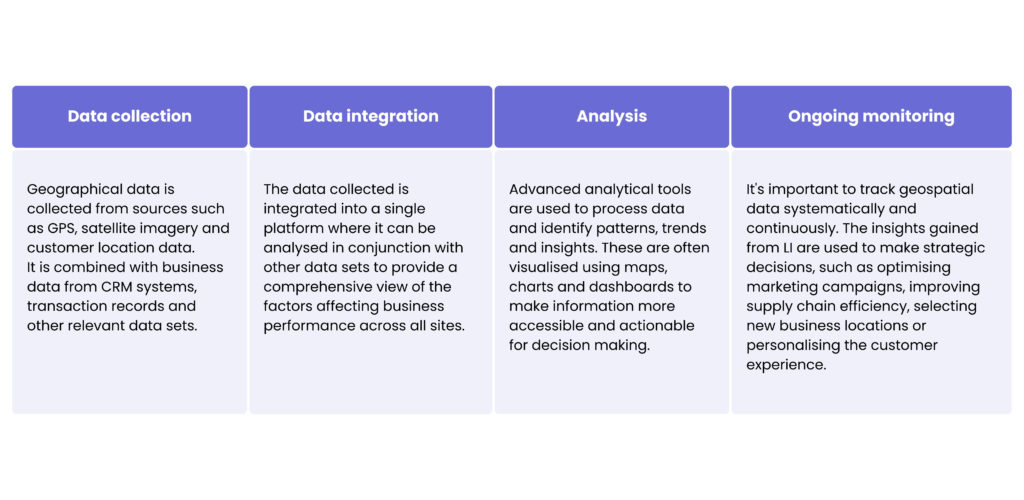
The process typically involves several key steps:
The role of location in addressing modern challenges
The challenges we encounter in business and government are inextricably linked to geography. It provides critical insight into a range of key issues, including infrastructure development, sustainability, climate change, environmental protection and social equity.
- The importance of location data is growing – Location information has always been vital, but now, with billions of sensors and smart devices, the amount of data available for visualisation and analysis has increased significantly.
- It has applications across all sectors – From government to real estate and retail, location intelligence is driving everything from supply chain optimisation to climate resilience.
- Location intelligence is essential – Without location-based analytics, we miss out on the key information and insights needed to take more effective and informed action.
“Advanced location intelligence technology, powered by machine learning and big data, allows us to turn raw spatial data into actionable insights at an unprecedented scale. This is accelerating the pace of smart city innovation and improving our ability to proactively respond to challenges such as climate change, infrastructure management and public health crises.”
Jaroslaw Marciniak, Director of Geospatial Services
Location intelligence real-world use cases
Transportation & urban planning
Analysing real-time geospatial data can facilitate intelligent transport in urban areas. By using location intelligence, traffic data is used to improve traffic flow, reduce congestion and reduce emissions. In addition, location intelligence supports applications that provide real-time updates on public transport arrivals and notifies users of maintenance disruptions.
Agriculture
Smart agriculture uses location intelligence in many ways. For example, soil moisture data from sensors can be combined with weather forecasts to provide intelligent irrigation recommendations and optimise water use. Location data from sensors attached to livestock can monitor their activity, providing insights into behaviour and land use.
Supply chain management
In this case, LI can be used for routing and workforce optimisation. By using location data, companies can streamline fleet management and improve driver efficiency. In addition, network optimisation and site selection enable retailers to choose warehouse locations closer to customers, thereby reducing delivery times.
Climate change mitigation
Key drivers of climate change such as CO2 emissions, coral reef health, ocean temperatures and sea levels can be monitored and analysed using geospatial information. GIS enables risk visualisation and supports decisions on climate change mitigation. In addition, identifying and predicting weather conditions and climate risks can help select the best locations for renewable infrastructure, such as wind turbines or solar panels.
See our geospatial offerings!
Find out moreStrategic benefits of LI technology for your business
Location Intelligence technology offers a wide range of advantages for business that can significantly improve operations or strategic planning and drive business efficiency.
Understand the customer better
Location intelligence technology enables companies to gain a deeper understanding of customer behavior by analysing location-based data. Acquisition of this knowledge helps identify customer preferences, predict trends, and more accurately segment markets, leading to more targeted strategies and improved customer satisfaction.
Optimised logistics & operations
By integrating geographic and operational data, LI helps companies streamline logistics and supply chain management. It enables efficient route planning, reduces transportation costs, and improves inventory management, ultimately leading to better resource allocation and operational efficiency.
New market expansion opportunities
LI provides valuable data to select optimal locations for new stores, facilities, or branches. By analysing factors such as demographics, competitor locations, and market demand, companies can make informed decisions about where to expand, maximising their market potential and minimising risk.
Better decision-making with predictive analytics
Using historical location-based data, the technology allows companies to predict future trends and behaviours. With its predictive capabilities, businesses are able to make more strategic decisions like anticipating market changes, optimising product offerings, and preparing for potential challenges, outpacing the competition.
The upcoming trends of intelligent localisation
As businesses adopt data and advanced analytics, they are increasingly recognising the unique value of physical location, as most data points have a location component. By linking data with geospatial context, businesses can gain deeper insights into customer behaviour, lifestyles or needs. The importance of location intelligence will continue to grow in the coming year, driving new trends and applications across multiple sectors.
Data enrichment for better AI outcomes
The effectiveness of Geo AI depends on high-quality data, and enriching data with third-party datasets and spatial insights improves accuracy and usability, leading to better results, cost savings, and deeper insights into consumer behaviour when location data is integrated.
Location Intelligence as a key differentiator
Location Intelligence is essential for reducing risk, improving customer satisfaction and maximising resources, offering high returns on modest investments in sectors such as telecommunications, financial services and insurance.
Democratising location intelligence
With the widespread availability of LI tools through smartphones, consumers now have real-time tracking, live traffic updates and enhanced navigation at their fingertips, while businesses continue to seek more accessible and user-friendly LI solutions to streamline decision-making.
Driving data integrity
The 2023 Data Integrity Trends and Insights Report emphasises that trusted data is critical, with 77% of professionals surveyed relying on location data to make important decisions. However, only 46% rate their data quality as high and 41% cite poor address data quality as a barrier, highlighting the need to address data quality issues and implement strong data governance to fully leverage location data for competitive advantage.
Over to you
Integrating location intelligence into business operations is essential for business leaders seeking greater efficiency and optimisation. With the right tools, data and mindset, the possibilities for businesses using location intelligence are limitless.
If you’d like to explore how location intelligence can help your business succeed, contact our geospatial experts directly using the form below!
About the author
contact us
Let’s get in touch to check how our experts could support your project
Recommended articles