What is Automotive SPICE® Potential Analysis 2024 and how will it affect the industry?
The automotive world is rapidly transforming, with software taking the driver’s seat in shaping functionality and innovation. In this landscape, the question of whether suppliers can keep pace is more pressing than ever. Automotive SPICE® Potential Analysis (PoA), introduced in 2024 by the VDA QMC — the Quality Management Centre of the German Association of the Automotive Industry —offers a fresh lens for examining technical readiness. As a key organisation shaping quality standards in the automotive sector, the VDA QMC develops frameworks to foster consistency, reliability, and technical excellence. This new approach is quietly but firmly reshaping the dynamics between OEMs and suppliers, laying the groundwork for partnerships built to thrive in a software-led future.
Automotive SPICE Potential Analysis 2024: a new topic in the industry
As the Automotive industry pivots towards software-defined vehicles, Automotive SPICE PoA emerges as a timely and innovative tool. It evaluates the capability of collaborations or partnerships in delivering a specific planned product or service. Introduced in 2024, it bridges the gap between traditional evaluations and the need for swift, software-focused assessments. Automotive SPICE PoA is poised to become a game-changer in supplier evaluations.
Get free Guide to Automotive SPICE ebook
Download nowThe connection to VDA QMC standards
Automotive SPICE PoA shares similarities with the VDA 6.3 Potential Analysis, particularly Module P1, which has long been recognised for risk assessments. Traditionally, VDA 6.3 evaluates risks related to suppliers, technologies, production sites, and products. However, while VDA 6.3 encompasses a broad range of domains, Automotive SPICE PoA takes a more specialised approach.
Focusing exclusively on software systems, Automotive SPICE PoA serves as an independent Process Assessment Model (PAM)/Process Reference Model (PRM). Unlike VDA 6.3, it does not assess hardware or mechanical aspects, offering a targeted evaluation that meets the specific needs of modern Automotive software projects. This specialised approach is built on a standardised method, which is crucial for evaluating the capabilities of potential collaborations for product or service delivery, reducing risks, and facilitating process improvements.
Assessment vs. potential analysis – key evaluation differences
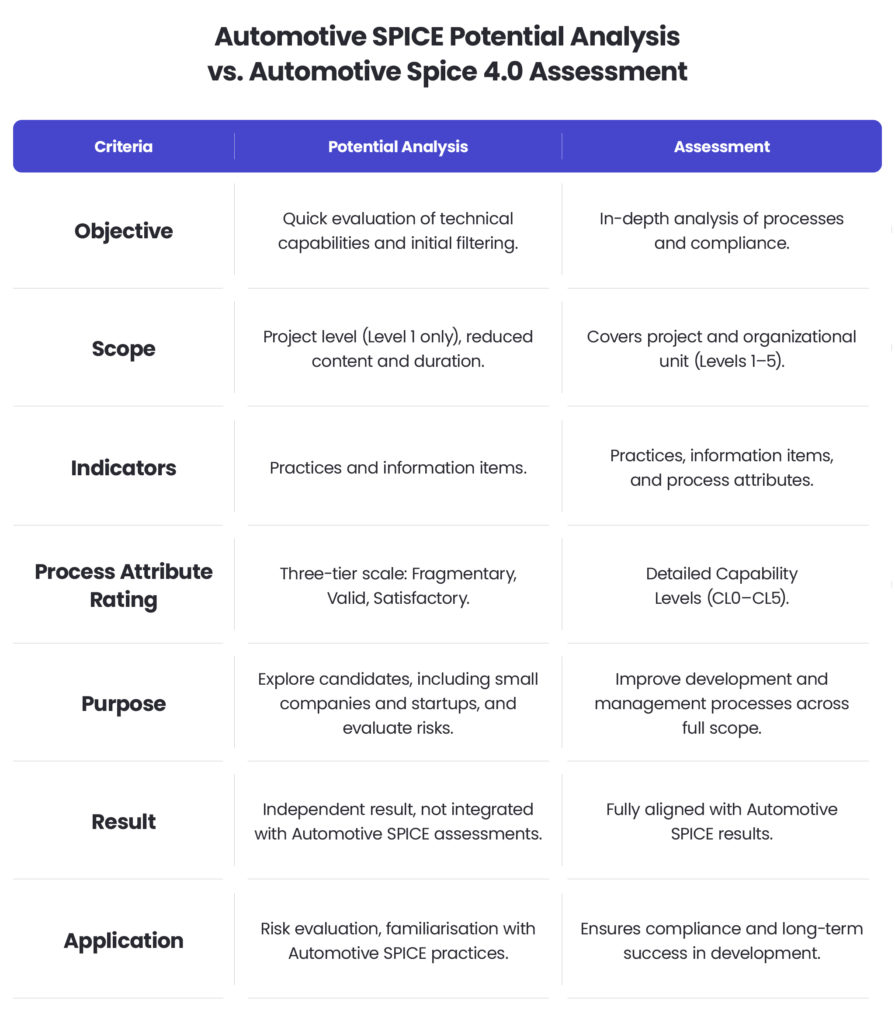
Automotive SPICE PoA and full Automotive SPICE® 4.0 assessments differ significantly in their scope, purpose, and application. These distinctions are summarised below:
In the case of specific assessments and evaluations, understanding or validating various Automotive SPICE models and guidelines becomes crucial. Automotive SPICE PoA is particularly effective in early project phases or scenarios requiring rapid evaluations, while full Automotive SPICE assessments remain indispensable for comprehensive process analysis.
Process Reference Model (PRM) in Automotive SPICE PoA
The Process Reference Model (PRM) in Automotive SPICE PoA is derived from Automotive SPICE® 4.0, retaining its methodological foundation while streamlining the structure for quicker assessments. Focusing on Capability Level 1, PRM evaluates critical technical processes while excluding non-essential organisational aspects.
Support plays a crucial role in facilitating process improvement and problem analysis efforts within the framework of Automotive SPICE PoA.
Structure of PRM in Automotive SPICE PoA:
1. BASIC Scope: Mandatory core processes, including:
- Potential Project Management (POPM),
- Release and Technical Configuration Management (RTCM),
- Process Quality Assurance (PQAS),
- Technical Problem Resolution (TEPR).
2. PLUG-IN: Optional processes to extend the assessment in areas such as:
- System Level: System Requirements and Design (SYRD), System Integration and Verification (SYIV),
- Software Level: Software Requirements, Design and Implementation (SWDI), Software Integration and Verification (SWIV),
- Requirements Elicitation: Gathering and managing stakeholder requirements (REEL).
3. FLEX Scope:
Additional processes tailored to specific project needs, such as Partner and Collaboration Management (PCOM) or Technical Change Request Management (TCRM).
Practical applications
Automotive SPICE PoA finds its strength in practical, early-phase applications. For instance, imagine an OEM working on a next-generation ADAS project. By leveraging Automotive SPICE PoA, the OEM can quickly evaluate multiple suppliers’ software development capabilities, ensuring they align with project needs. This evaluation includes assessing potential collaboration to ensure that partnerships are capable of effectively delivering planned products or services.
Similarly, suppliers can use Automotive SPICE PoA to identify gaps in their processes, such as inadequate traceability in testing, before presenting their readiness to OEMs. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks but also fosters stronger collaboration and confidence between stakeholders. It helps realise the capabilities of partners to effectively deliver planned products or services while addressing constraints and improving processes.
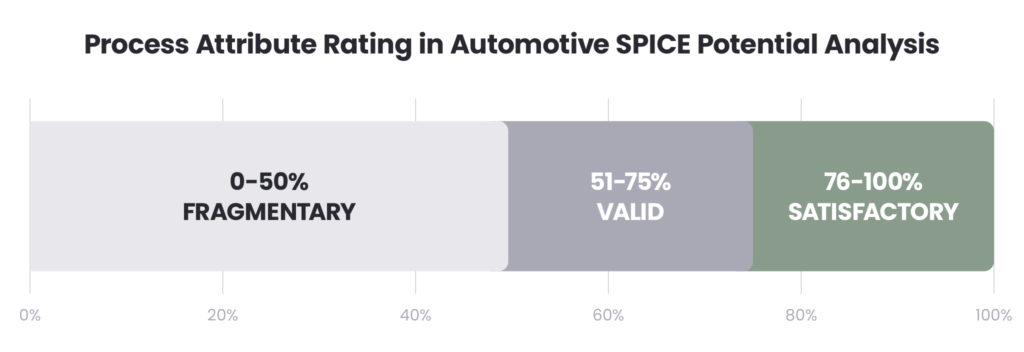
Process Attribute Rating in Automotive SPICE PoA
Automotive SPICE PoA employs a simplified three-tier rating system to assess process outcomes:
1. Fragmentary (light grey):
- Reflects insufficient evidence or partial implementation.
- Achievement level: 0–50%.
2. Valid (dark grey):
- Indicates that most outcomes are met, though gaps remain.
- Achievement level: 51–75%.
3. Satisfactory (green):
- Demonstrates full achievement, with negligible gaps.
- Achievement level: 76–100%.
This system simplifies the evaluation process while identifying critical areas for improvement early in the project lifecycle. It is important to confirm user agreement to document license rules, ensuring compliance and understanding of the terms associated with the document.
Impact of Automotive SPICE PoA
Automotive SPICE PoA has the potential to reshape the automotive industry by fostering clarity, trust, and precision across all stages of development. For suppliers, it provides a roadmap to align with OEM expectations, highlighting areas for improvement and building readiness for complex projects. Successfully completing an Automotive SPICE PoA assessment enhances confidence and facilitates long-term partnerships with OEMs.
OEMs benefit from reduced risks through early evaluations of suppliers’ technical capabilities. The streamlined approach simplifies supplier selection while ensuring high-quality, innovative solutions. Automotive SPICE PoA also fosters collaboration, enabling OEMs and suppliers to address deficiencies jointly and strengthen their relationships.
For end users, Automotive SPICE PoA contributes to safer, more reliable vehicles. The robust software systems it promotes enable advanced features such as ADAS and connectivity solutions. By emphasising safety and traceability, Automotive SPICE PoA builds confidence in the reliability and innovation of Automotive systems, shaping a future driven by quality and trust.
Summary and challenges
Automotive SPICE® Potential Analysis 2024 is more than a tool; it’s a response to the Automotive industry’s shift toward software-first development. By focusing on evaluating the capabilities of potential partners to execute and deliver planned products or services, ensuring consistency, traceability, and effective process assessment. Automotive SPICE PoA bridges the gap between supplier readiness and OEM expectations. However, as a new methodology, its adoption will require time, training, and a willingness to adapt.
It is crucial for users to agree to the document license rules, emphasising the importance of compliance and user consent in the processes.
While Automotive SPICE PoA is optimised for early-phase evaluations, organisations must balance its efficiency with the deeper insights offered by full Automotive SPICE assessments when needed. Successfully navigating these scenarios will allow Automotive SPICE PoA to establish itself as an indispensable tool in supplier evaluations, shaping a future of safe, innovative, and high-quality Automotive systems.
About the author
Contact us