Augmented reality 101: use cases and future predictions
The potential of augmented reality spans various industries, from retail and manufacturing, to even healthcare. As AR technology is constantly being improved, its application extends way beyond games and virtual entertainment.
In this article, we’ll look at how augmented reality works to understand better what it can be used for. Then, we’ll also describe some current and evolving augmented reality use cases in business as well as discuss how AR will be developing in the future.
What is augmented reality in simple words?
Augmented reality (AR) is a way to present extra data through digital visual elements, sound or sensory stimuli in a real world environment. AR usually layers virtual objects on top of real ones but can also hide virtual objects behind real ones or hide real objects, so they are not visible on the screen. The evolution of AR technologies has significantly transformed various industries by enhancing customer engagement and experience.
Brief history and evolution of AR
Augmented reality has a fascinating history that dates back several decades. The concept of AR was first introduced in the 1960s, but it wasn’t until the 1990s that the first practical AR applications began to emerge. These early applications were primarily focused on education, training, and gaming, laying the groundwork for the technology we know today.
The 2000s marked a significant turning point for AR technology, driven by the rapid development of smartphones and tablets. This era saw the creation of AR apps that could be used on mobile devices, bringing AR into the mainstream. Popular apps like Pokémon Go and Snapchat showcased the potential of AR for entertainment and social interaction, capturing the imagination of millions worldwide.
Today, AR technology is being harnessed across a wide range of industries, from education and healthcare to marketing and retail. Businesses are leveraging AR to enhance customer experiences, improve training and education, and foster greater engagement and interaction. The journey of AR from a conceptual idea to a transformative technology is a testament to its incredible potential and versatility.
How does augmented reality work?
The way augmented reality works depends on the complexity of the system. In general, AR uses computer vision, GPS data about user localisation, mapping and depth tracking to show extra data layered on the real-world context. The cameras and sensors collect, send and process the gathered data to show virtual content layered on what the user is looking at in real time. As the user moves, the AR visuals automatically adjust to the changed context.
The hardware components required for augmented reality include: a processor, display (optical projection systems, monitors, wearable display devices, eyeglasses or goggles), sensors and input devices. Smartphones and mobile tablets are commonly used for AR as they are very often equipped with sensors, like accelerometer, GPS or compass that allow motion tracking. However, the more complex the AR, the more computing power the processor should have, as the latency requirements are extreme. In mobile devices, insufficient computing power is often compensated by offloading data processing to a remote machine in the cloud.
What does merging reality with a digital world looks like?
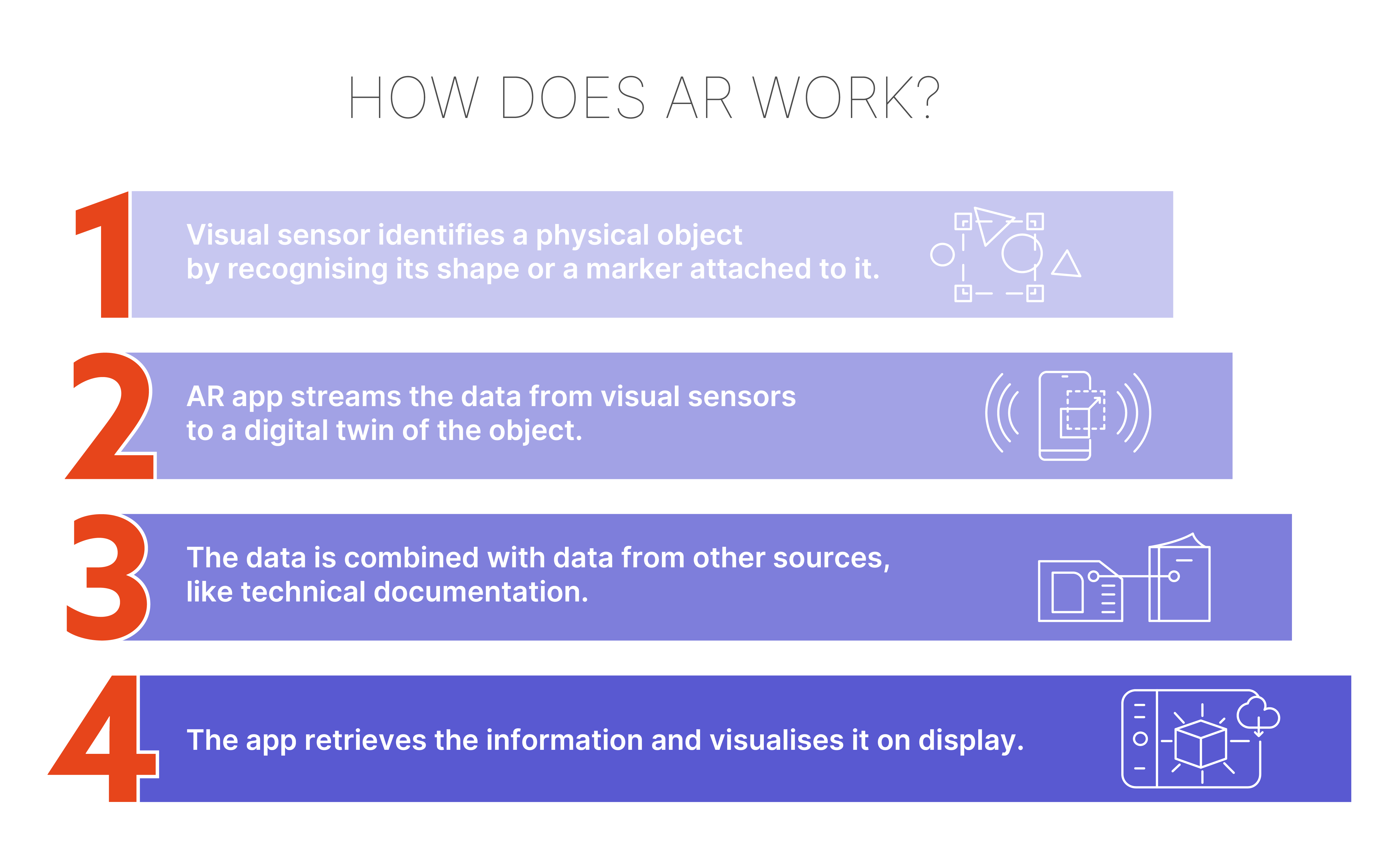
Let’s illustrate how AR works in an industrial manufacturing context. Let’s imagine a situation, in which AR enables workers to get trained by substituting paper manuals with digital instructions presented directly in their field of view, for example, through AR goggles, leaving their hands free and reducing mental effort required to operate a machine.
The AR-enabled device uses a visual sensor to identify a physical object by recognising its shape or a marker attached to it. Then, the AR application connects with a digital twin (a 3D copy) of the object – in our example, one of the machines used on the production line. The data from visual sensors is then streamed to a digital twin and is combined with data from other sources, like technical documentation. The application retrieves the information and visualises it to the user on display, in some cases allowing the user to interact with the visualisation through touch interaction.
That’s just one of the examples of how augmented reality is used in a business context. In recent years, AR has been spreading across many industries, from entertainment to healthcare. Below you can read about a handful of other applications.
Differences between augmented reality and virtual reality
While augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are often mentioned in the same breath, they are distinct technologies with unique applications. Virtual reality creates a completely immersive digital environment that replaces the physical world, transporting users to a different reality altogether. In contrast, augmented reality enhances the physical world by overlaying digital information and images onto it, creating a blended experience.
VR is predominantly used for gaming, education, and training, offering users a fully immersive experience. On the other hand, AR is utilised in a broader range of applications, including marketing, retail, and healthcare. One of the key advantages of AR is its accessibility; it can be used on a wide variety of devices, such as smartphones and tablets, making it more readily available to the general public.
Understanding the differences between AR and VR is crucial for appreciating the unique benefits each technology offers and how they can be applied to various fields.
Check our human-machine interface consulting and development services
Learn moreWhat are some examples of augmented reality use?
The beginnings of AR technology are grounded in aviation, where it’s still used, for example, in pilot training. AR head-up displays are also used in military aircraft to present flight parameters and machine controls right in the field of a pilot’s view, so they can remain focused on piloting the aircraft.
Head-up displays have been then transferred to automotive vehicles. Originally, car head-up displays presented data, such as the speed or a route map. These days, thanks to AR, the data, such as navigation, is displayed on the real-life view of the road, instead of just a map.
Another example of an industry where AR is widely used is entertainment. The global AR market reached a value of US$ 6.39 Billion in 2021 and is expected to reach $ 38.03 billion by 2027. Augmented reality is more and more common in sports. During live sports coverage, augmented reality can enrich the play-by-play with extra data. For example, in golf, using special technologies (see our TrackMan case study), it’s possible to track a ball’s flight path, speed, the exact point where it hit the ground etc. and display this information on the screen in real time.
AR also has the potential to revolutionise medicine, though it is currently regarded as a novelty. The research is conducted on the possible use of AR to provide medical imaging data in the operation area or to train surgeons.
What are the benefits of augmented reality?
AR reduces cognitive overload
AR provides necessary information exactly when the user needs it by strategically deploying augmented reality features. There’s no need to reach for extra resources.
AR enriches reality
Augmented reality applications add a layer of extra information to the real world around us, enriching the user experience and helping to understand the surrounding world better.
AR improves accessibility and reduces barriers
AR devices and applications can serve as instructional tools for people with disabilities performing certain real-world tasks. Haptics and audio feedback allow people with visual or cognitive impairments to use touch and hearing to understand information about the surrounding world in real time, thus making it more accessible to them.
AR allows the visualisation of abstract ideas in real world environment
It’s one of the most ground-breaking benefits of AR that’s especially valuable in the retail industry. Customers don’t have to rely solely on their imagination to decide which colour or pattern of a sofa best matches their interior design or how a particular model of a watch will look on their wrist.
The future of Augmented reality is looking bright
Augmented reality continues to evolve, with mobile AR taking the market by the storm. Mobile devices are being equipped with new technologies, like LiDAR, that can significantly boost AR capabilities by adding more depth and allowing for occlusion, making the AR experiences feel more natural.
According to the Grand View Research report, the AR market size, estimated at USD 25.33 billion in 2021, is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 40.9% from 2022 to 2030. The industrial and manufacturing segment is accounted for the largest revenue share and is predicted to continue dominating the market in this decade. Also, the automotive industry is widely adopting AR technology to enhance user experience and its market share is estimated to grow by 43.3%. The use of AR in the healthcare segment is expected to skyrocket in the near future as it’s increasingly being implemented in training and surgical visualisation.
The time to adopt AR technology is now. Tell us about your needs and idea, and we’ll help you build a cutting-edge AR solution.
About the author
RECOMMENDED READING:
CONTACT US




